Study on the grain orientation effect on the microstructure evolution and failure in interconnects in advanced packaging structures
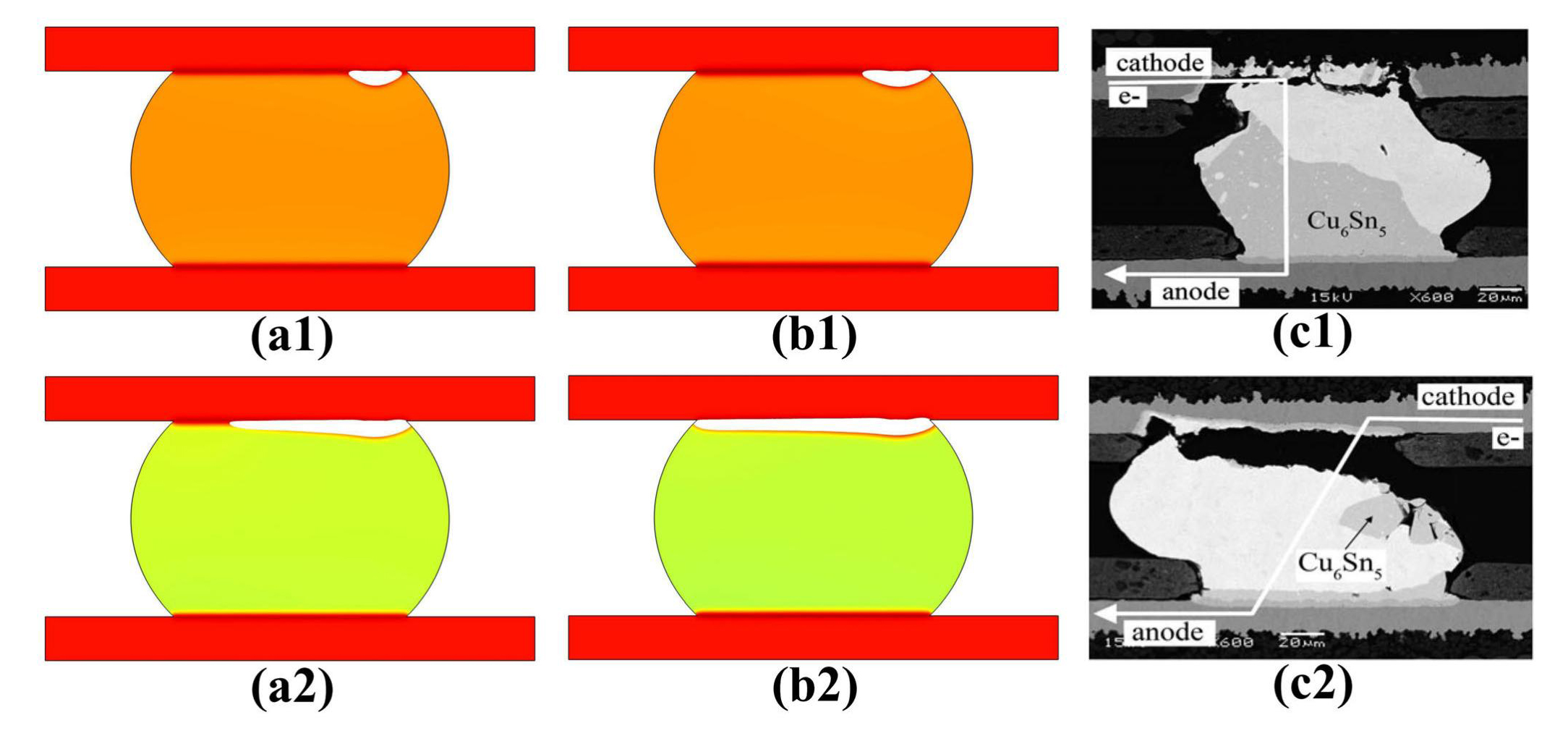
In this research topic, we developed phase field model to simulate and reveal the grain orientation effect on the microstructure evolution and failure mechanism in solder interconnects. Due to the small size of interconnects in 3D ICs and complicated electric-mechanical-thermal coupled loads, the grain size and distribution have a significant influence on the performance of the interconnects in service, and experimental studies have lots of challenges to dynamically track the microstructure evolution and degradation process. The developed model could simulate and reveal the interaction effects between microstructure change and field response. Some cases of these works can be found at S Liang et al., 2023, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices and S Liang et al., 2021, Scripta Materialia.
Thermo-mechanical characteristics and reliability of die-attach through SPER bonding for power electronics
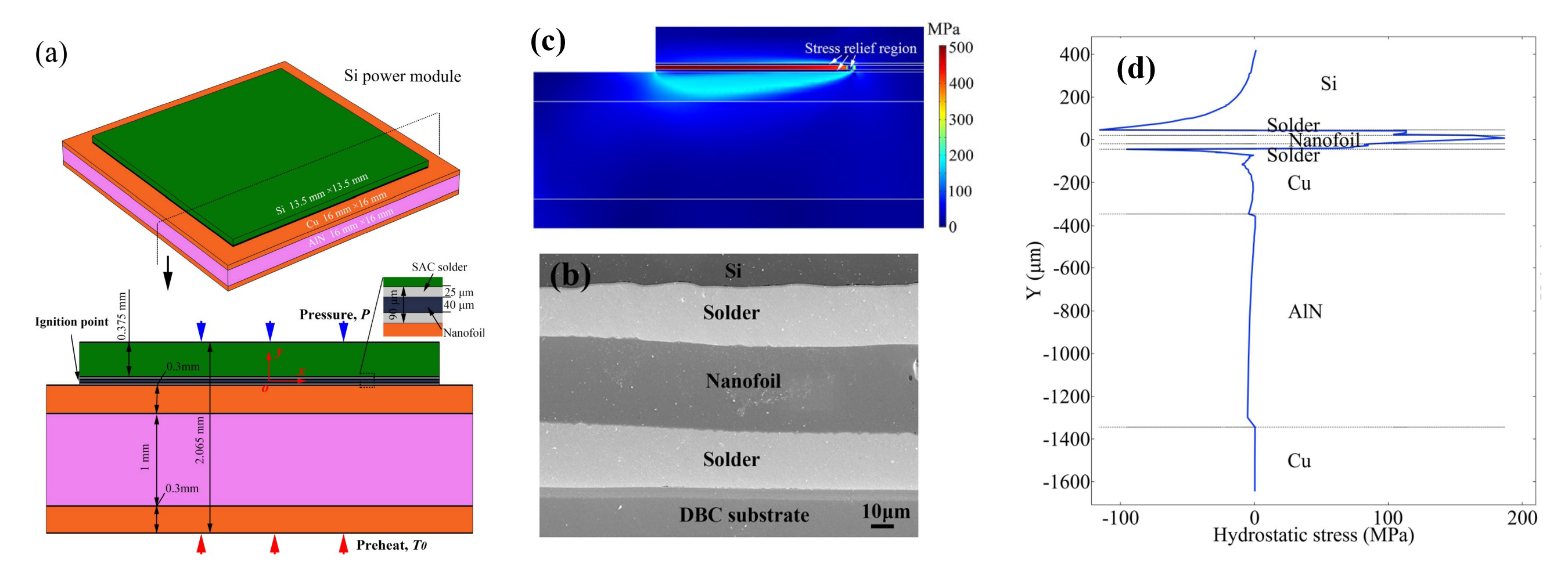
Self-propagating exothermic reactions (SPERs) provide intense localized heat sufficient for bonding metals or alloys with minimal heat excursion to the components. In this research work, finite element analysis combined with experiment are performed to understand the thermal transfer and mechanical responses of materials to the SPER bonding for the die-attach of Si device onto direct bonded copper (DBC) substrate with Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC) solder. A systematic investigation on the mechanical responses due to thermal mismatch reveals their effects on the thermal stress of interfaces and bonding reliability. Some cases of these works can be found at S Liang et al., 2021, IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology and S Liang et al., 2020, ECTC.
In this research topic, we developed phase field model to simulate and reveal the grain orientation effect on the microstructure evolution and failure mechanism in solder interconnects. Due to the small size of interconnects in 3D ICs and complicated electric-mechanical-thermal coupled loads, the grain size and distribution have a significant influence on the performance of the interconnects in service, and experimental studies have lots of challenges to dynamically track the microstructure evolution and degradation process. The developed model could simulate and reveal the interaction effects between microstructure change and field response. Some cases of these works can be found at S Liang et al., 2023, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices and S Liang et al., 2021, Scripta Materialia.
Thermo-mechanical characteristics and reliability of die-attach through SPER bonding for power electronics
Self-propagating exothermic reactions (SPERs) provide intense localized heat sufficient for bonding metals or alloys with minimal heat excursion to the components. In this research work, finite element analysis combined with experiment are performed to understand the thermal transfer and mechanical responses of materials to the SPER bonding for the die-attach of Si device onto direct bonded copper (DBC) substrate with Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC) solder. A systematic investigation on the mechanical responses due to thermal mismatch reveals their effects on the thermal stress of interfaces and bonding reliability. Some cases of these works can be found at S Liang et al., 2021, IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology and S Liang et al., 2020, ECTC.